
views
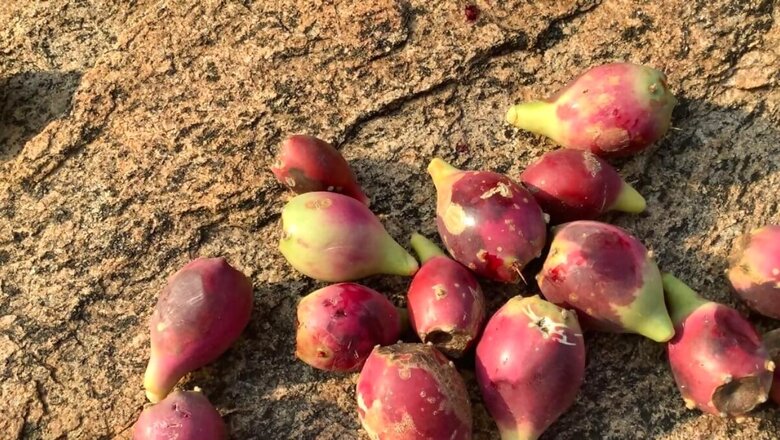
The prickly pear cactus, scientifically known as Opuntia ficus-indica, belongs to the Cactaceae cactus family. It is also known by various names such as nopal, tuna, sabra, and paddle cactus. This cactus features broad and flat green pads, often called nopales, which are widely consumed. Nopales are utilized in Mexican cuisine, and incorporated into dishes like egg dishes, salads, tacos, and soups.
Prickly pear can be observed growing in a variety of environments, including washes, rocky hillsides, areas surrounding boulders, as well as regions characterized by sandy or gravelly soil conditions.
This fruit is also known as Indian Kiwi and is mostly grown in Erode, Kodumanal region, Tamil Nadu. Prickly pears have a slightly varied nutritional profile depending on the specific type, but in general, they are a good source of fibre and offer a range of vitamins and minerals.
A single cup (149 grams) of raw prickly pear contains approximately 61 calories, 1 gram of protein, 1 gram of fat, 14 grams of carbohydrates, 5 grams of fibre, and notable amounts of magnesium (30% DV), vitamin C (23% DV), potassium (7% DV), and calcium (6% DV).
Due to its exceptional ability to withstand drought, it is advisable to provide the prickly pear cactus with less water than it initially requires. In most regions, regular rainfall is usually sufficient for the cactus to flourish.
Prickly pear is often hailed for its potential benefits in promoting radiant skin and lustrous hair. Its extracts are incorporated into hair conditioners and skincare products due to their advantageous properties. Certain components and nutrients found in prickly pears, such as vitamin C and betalain pigments, possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Furthermore, the fruit contains polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly in its seeds and peel, which contribute to the health of the skin and hair.
Prickly pear has the potential to offer advantages in blood sugar control and managing diabetes-related complications. Pectin, a soluble fibre found in prickly pears, has been linked to lowering blood sugar levels and improving blood fat levels.
Early human studies indicate that consuming prickly pear may lead to a fall in blood sugar levels and insulin levels after meals, benefiting both individuals with type 2 diabetes and healthy adults.



















Comments
0 comment