views
Making CO2 At Home
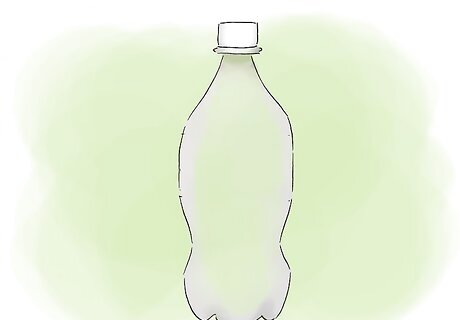
Get a 2-liter plastic bottle. Use plastic instead of glass; if you should build enough pressure to rupture the bottle, a plastic bottle will not explode the way a glass bottle would. If you're planning to use the generated CO2 to supply carbon dioxide for the plants in your aquarium, a bottle of this size will provide an adequate supply for a 25-gallon (94.64 l) aquarium.

Add 2 cups (473.18 ml) of sugar. Use raw instead of refined sugar, as it has more complex sugars that will take longer for the yeast to break down. It's also cheaper.
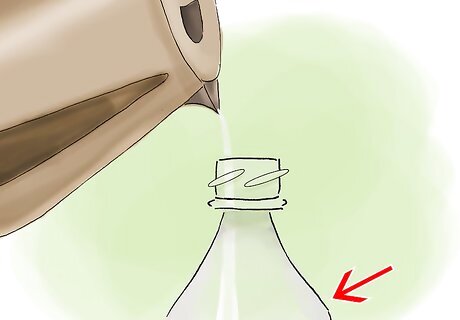
Using warm water, fill the bottle to where it starts to curve toward the neck. Warm tap water is sufficient; hot water will kill the yeast.

Add 1/2 teaspoon (2.46 ml) of sodium bicarbonate. Sodium bicarbonate is the principal ingredient in baking soda, available at most stores.

Add 1/2 teaspoon (2.46 ml) of any yeast extract. If available, this will help the yeast last longer. An example of a yeast extract is Vegemite, found in Australia. Other yeast extracts include Bovril, Cenovis, and Marmite.

Add 1/3 teaspoon (1.64 ml) of yeast. Brewer's yeast lasts longer than baker's yeast, but baker's yeast lasts long enough for the reaction and is cheaper than brewer's yeast.

Cap the bottle securely.
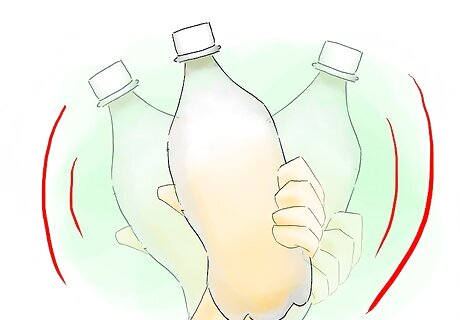
Shake the bottle to thoroughly mix the yeast and sugar. You should see a slight foaming at the top of the water.
Uncap the bottle.

Wait 2 to 12 hours. The water should start to bubble during this time, showing that CO2 is being released. If you don't see bubbling after 12 hours, you either had the water too hot or your yeast is no longer active. Your solution should bubble at about the rate of 2 bubbles every second. Any faster, and you may upset the pH of the water.
Other Ways CO2 is Produced

Exhale. Your body uses the oxygen you inhale to react with the proteins, fatty acids, and carbohydrates you ingest. One of the results of this reaction is the carbon dioxide you exhale. In contrast, plants and some forms of bacteria take carbon dioxide from the air and, with energy supplied from sunlight, make simple sugars (which are carbohydrates).

Burn something with carbon in it. Life on Earth is based on the element carbon. To burn something requires a spark, a fuel source, and an atmosphere to burn it in. The oxygen in our atmosphere readily reacts with other substances; put it with burning carbon, and you get carbon dioxide. Calcium oxide (CaO), also known as quicklime, can be produced by burning limestone, which contains calcium carbonate (CaCO3). The CO2 is driven off, leaving the calcium oxide. (For this reason, it is also called burnt lime.)
Mix carbon-containing chemicals. The carbon and oxygen that make up CO2 are found in a number of chemicals and minerals classified as carbonates or, when hydrogen is also present, bicarbonates. Reactions with other chemicals can release CO2 into the air or mix it with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3). Some of the possible reactions include the following: Hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is the acid found in the human stomach. Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is found in limestone, chalk, eggshells, pearls, and coral, as well as some antacids. When the two chemicals are mixed, calcium chloride and carbonic acid are formed, and the carbonic acid breaks down into water and carbon dioxide. Vinegar and baking soda. Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid (C2H4O2), while baking soda is sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). Mixing them produces water, sodium acetate, and CO2, usually in a foamy reaction. Methane and water vapor. This reaction is performed industrially to extract hydrogen by using steam at high temperatures. The methane (CH4) reacts with the water vapor (H2O) to produce hydrogen (H2) and carbon monoxide (CO), a deadly gas. The carbon monoxide is then mixed with water vapor at lower temperatures to produce more hydrogen and turn the carbon monoxide into safer carbon dioxide. Yeast and sugar. When yeast is added to sugar in solution, as in the instructions in Part One, it forces the sugar to break down and give off CO2. The reaction also produces ethanol (C2H5OH), the form of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages. This reaction is called fermentation.



















Comments
0 comment