
views
Using Verified Medical Treatments

Talk to your dermatologist about prescription skin medications. Oftentimes, you can get rid of a vascular birthmark (such as hemangiomas) by taking corticosteroids. Corticosteroids slow down the development of birthmarks and reduce their size but they do not actually remove the mark. Corticosteroids can be taken orally, injected into the birthmark, or used topically. Other medications used for birthmarks include propranolol and vincristine, which are used for hemangiomas (see the last section below for more details).
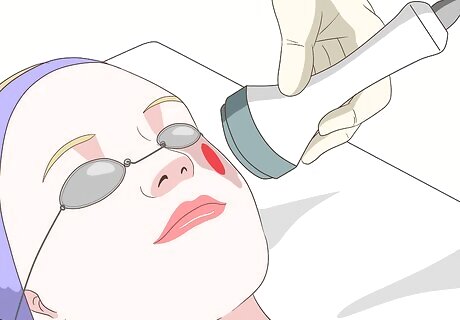
Investigate laser therapy. Laser therapy can help to reduce the size and halt the development of vascular birthmarks. Laser therapy involves the application of focused, short laser light bursts to the birthmark and can be used to lessen the color, reduce the size, and even stop certain birthmarks from growing. Laser therapy can be used to remove port-wine stains and café au lait spots but is not always successful, causing the spots to return. Although total removal of birthmarks may be impossible, they can be lightened considerably after several sessions of laser therapy. Laser therapy can be an effective treatment method, but it can also be very expensive.
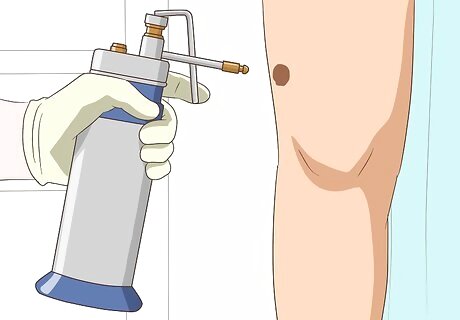
Consider cryosurgery to remove birthmarks. Cryosurgery uses liquid nitrogen to freeze and fade spots, causing them to peel off. During the procedure, liquid nitrogen is applied on the mark to freeze the skin on and under the spot. Then, the skin is scraped off using an instrument known as curette. Complications of cryosurgery include scarring and lightened skin color.
Look into surgical excision. Skin surgery can be done as an outpatient procedure and only involves a removal of very limited amounts of outer skin. Although surgical removal of skin is considered a minor procedure, it is still invasive and a preoperative assessment of the patient should be done by the doctor. Surgery can be done to remove moles and hemangiomas Depending on the size of the birthmark, surgery may leave a permanent scar. During the procedure, your doctor will provide a local anesthesia to numb the area and then removes the birthmark with a scalpel. The skin is then stitched together using dissolving suture. Surgical excision is often intended for deeper birthmarks.
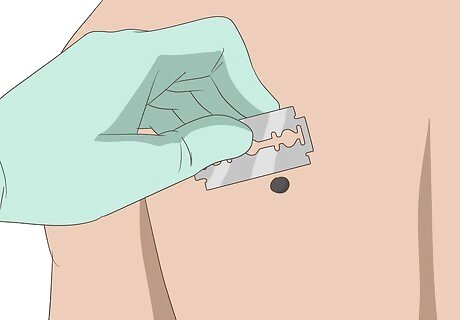
Ask about a surgical shave. A surgical shave is an incision done without the need for stitches. It is performed either through the use of a traditional blade or an electric cautery machine. During the procedure, your doctor uses local anesthesia to numb the area around the mark and then cuts the area around and beneath the birthmark with a small scalpel. Surgical shaving is often used for smaller moles or skin tags and rarely needs sutures.
Using Unverified Treatments
Use lemon juice to lighten skin. Lemon juice contains ingredients that can naturally lighten the skin. However, the efficacy of lemon juice in treating birthmarks has not been scientifically confirmed and thus, you should use this method with reservations. Apply fresh lemon juice on the birthmark for 20 minutes and rinse off. Repeat several times a week. Do not use if the lemon juice causes skin irritation. Keep in mind that you will probably have to repeat this treatment (or any home remedy) many times over many months to see an improvement. You may be better off speaking with a dermatologist about medical treatment options if you want to remove a birthmark.

Try iodine solution. Iodine may help fade birthmarks but again, this method has not been scientifically proven. Apply iodine solution over the spot twice daily. However, remember that iodine solution is a medical product and should be used with caution. Also, avoid using this treatment if you have an allergy to iodine or shell fish. Do not use if any irritation occurs and consult your doctor if you have any concerns.
Apply olive oil to moisturize your skin. Olive oil is a powerful natural moisturizer that can restore skin and make birthmarks appear softer and smoother. Apply olive oil at least three times over the spot, leave on to dry or rinse off. Use a cotton ball to apply the oil directly onto the birthmark 2 to 3 times a day.

Put tomato juice on your birthmark. Tomato juice has skin bleaching properties and may help fade birthmarks. Apply slightly warm tomato juice on the spot and let it air-dry. Repeat a few times a day for a month. Make sure that the tomato juice is not too hot or you may burn your skin.

Investigate vitamin A cream to promote skin cell regeneration. Vitamin A stimulates mitotic activity (cell division) and the production of collagen (the protein that builds the skin). Although vitamin A creams (often called Retinol) are used to treat hyperpigmentation, their efficacy in lightening birthmarks is not known.
Apply vitamin E oil onto the skin. The antioxidant properties of vitamin E may help with birthmarks. Mix vitamin E oil with orange oil and apply over the birthmark.
Identifying Your Birthmark
Know if your birthmark is a mole. A mole (also called congenital nevi) is a pigmented birthmark (caused by an overgrowth of the melanin-producing cells) on the skin that generally appears during childhood. The typical characteristics of moles include: Tan, brown, red, pink, blue or black color. Smooth, flat, wrinkled or raised texture. Oval to round shape. Typically less than 1/4 inch in diameter but sometimes moles can be bigger. Sometimes moles have hair growing on them. Most moles are harmless but in rare cases they can become cancerous. Monitor your moles and contact your doctor if their appearance changes.
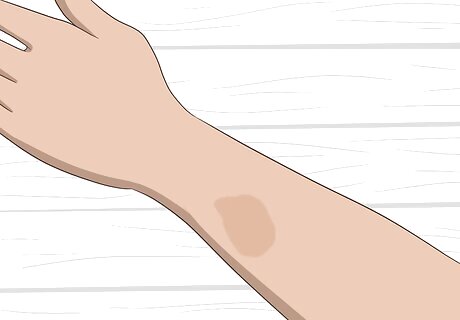
Identify if your birthmark is a café au lait. These pigmented birthmarks are sometimes caused by a genetic disorder called neurofibromatosis. This condition is divided into three distinct types; the mildest form (neurofibromatosis 1) appears in childhood and is characterized by flat, light brown-colored birthmarks on the skin: Café au lait spots can be present at birth or appear during childhood and then stabilize. They can be treated with lasers but often return. In addition to birthmarks, neurofibromatosis 1 may be characterized by freckling in the armpit, soft bumps on or under the skin (neurofibromas or benign tumors), tiny, harmless bumps on the eye (called Lisch nodules), and/or bone deformities. The two other types (neurofibromatosis 2 and 3) are much less common than the first type and are characterized by more serious symptoms and tumors. If you suspect your child has neurofibromatosis, consult the pediatrician. Neurofibromatosis can't be cured, but your child’s pediatrician will monitor the complications and treat the symptoms.
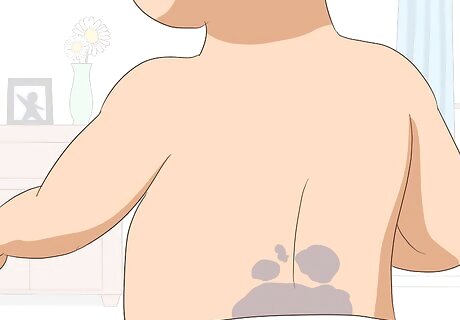
Know if you have Mongolian spots. These are pigmentation birthmarks in children that commonly disappear when the child reaches school age. Typical characteristics of Mongolian spots include: Blue or blue-gray-colored spots on the buttocks, back, spine, shoulders, or other areas. Flat and irregular shape. The skin texture is normal. Typical size is between 2 and 8 centimeters wide. Because these marks disappear on their own, no treatment is recommended.

Diagnose macular stains. Also known as salmon patches, stork bites or angel kisses, these are faint red vascular birthmarks (a result of blood vessels not forming correctly) most commonly present on the forehead, eyelids, back of the neck, nose, upper lip, or on the back of the head. They are characterizes by flat, light pink patches on the skin. Macular stains typically fade away on their own by the time your child is 1 to 2 years old but some may last into adulthood.
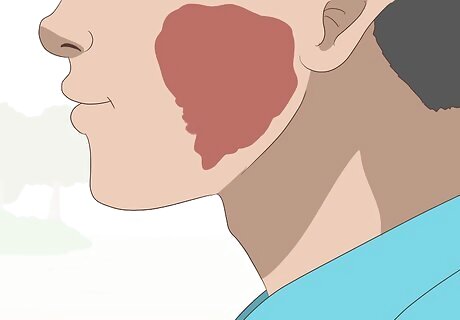
Spot a port-wine stain. This is a vascular birthmark that usually is permanent and does not disappear on its own. However, some treatments can make these marks less noticeable. Laser treatment, such as the pulsed dye laser, is the only way to reduce the appearance of port wine stains. Laser treatment can lighten the mark but often works better in children. You can also try to use cosmetics to hide these birthmarks if laser treatment proves unsuccessful.
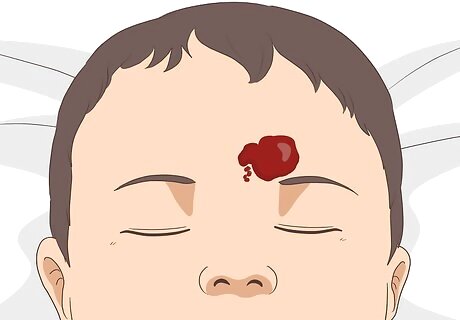
Identify if you or your child has hemangiomas. These are vascular birthmarks that appear within a couple weeks after birth and are often found on the head and neck. Hemangiomas are characterized by skin discoloration that may disappear within few months after birth or can take up to 12 years to fade away. Hemangiomas in the eye and mouth may cause complications, such as ulcers, and sometimes they can appear on the internal organs (stomach, kidneys and liver). Consult your doctor if you suspect your child has internal hemangiomas that may cause complications. Most hemangiomas can be treated or shrunk with medical treatment, such as oral propranolol, steroids or vincristine. In some cases, plastic surgery may be needed.


















Comments
0 comment