views
Measuring Brachial Pressure
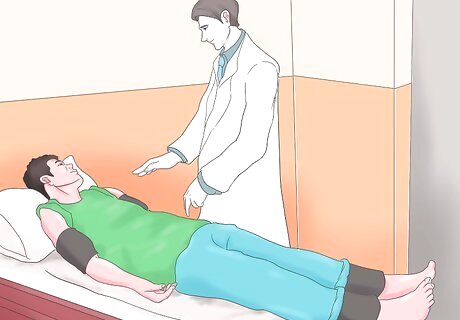
Ask the patient to lie down in a face-up position. Lying face-up is known as being in the supine position. Make sure that your patient is lying on a flat surface so that his arms and legs are at heart level. Give the patient at least 10 minutes of rest before taking his blood pressure. Resting will help his blood pressure to normalize, particularly is he is anxious, while also allowing the heart and brachial pulse to level out. Both of your patient’s arms should be exposed. Any sleeves should be rolled up loosely and out of the way.

Locate the brachial artery. Use your index and middle finger to locate the pulse site. Do not use your thumb because it has its own pulse that could make finding your patient’s pulse more difficult. The brachial pulse is usually felt just above the antecubital fossa--the middle part of the elbow bend.

Wrap the blood pressure cuff around the patient’s left arm. Make sure that the cuff is placed about two inches above the brachial pulse site. To avoid inaccurate readings, make sure that the the cuff is loose enough that it can rotate around the arm slightly, but not so loose that it could slip down the arm. If possible, use a blood pressure cuff that has a width that is approximately two-thirds of the length of the patient’s arm.

Inflate the cuff to find the systolic blood pressure of the arm. To take the blood pressure reading, place the diaphragm (circular piece) of the stethoscope on the brachial pulse. Close the valve of the hand-pump and use it to inflate the cuff to about 20 mmHg above regular blood pressure or until the pulsating sound or your patient’s pulse is no longer audible. Systolic pressure describes the maximum arterial pressure created by the contraction of the heart’s left ventricle. Diastolic pressure describes the minimum amount of pressure created when the ventricles fill with blood during the beginning of the cardiac cycle.
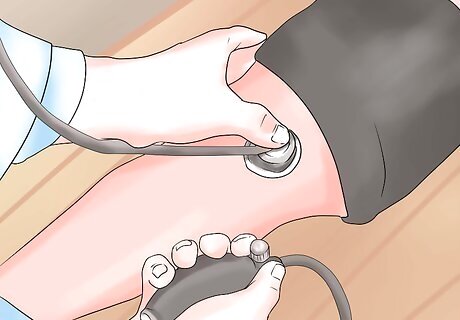
Deflate the cuff. Release the pressure slowly at a rate of 2 to 3 mmHg by opening the valve while closely monitoring the manometer (the pressure gauge). Take note when the pulsating sound returns, and again when it disappears--the systolic blood pressure is the point where the pulsating sound returns and the diastolic blood pressure is when the pulsating sound disappears. The systolic blood pressure is the value you will use later to calculate the ABI.
Measuring the Ankle Pressures
Ask your patient to remain lying face-up. The goal is to keep his arms and legs at heart-level so as to get the most accurate blood pressure reading. Remove the blood pressure cuff from your patient’s arm.
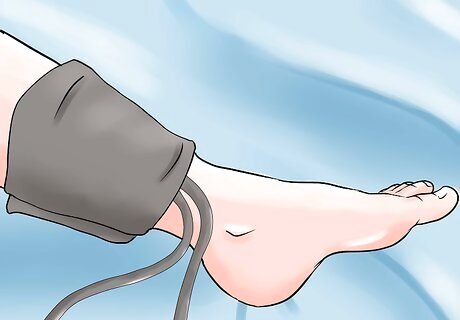
Wrap the blood pressure cuff around the patient’s left ankle. Position the cuff two inches above the malleolus (the bony knob) of the ankle. Make sure that the cuff is not wrapped too tightly. Check its tightness by inserting two fingers. If you can’t insert two fingers, then it is too tight. Make sure that you have the right sized cuff for your patient. The width of the cuff should be slightly wider than the diameter of the lower leg.
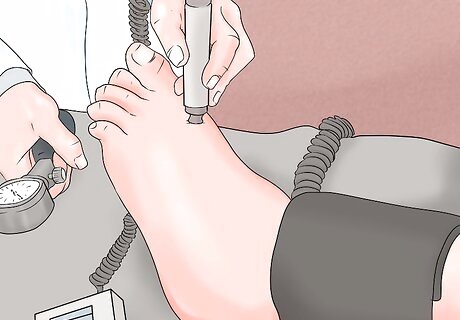
Locate the dorsalis pedis artery. The dorsalis pedis (DP) artery is located on the upper surface of the foot, right near where the foot meets the ankle. Spread ultrasound gel on this upper area of the foot. Use a Doppler probe to located the strongest point of the DP. Move the probe around until your find the spot where the pulse is the loudest. You should hear a pulsating or whooshing sound.

Record the blood pressure of the DP artery. Inflate the blood pressure cuff to about 20 mmHg above the patient’s regular systolic pressure or until the whooshing sound from the Doppler is gone. Deflate the cuff and take note when the whooshing sound returns. This is the systolic blood pressure of the ankle.
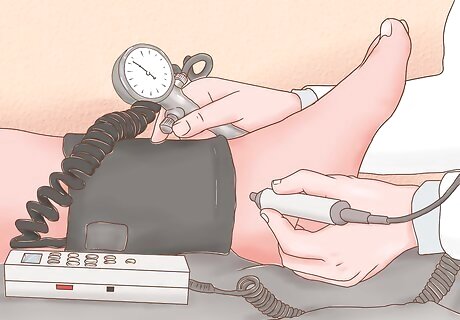
Find the posterior tibial (PT) artery. For the most accurate ABI, you should take the blood pressure of both the dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial arteries. The PT is located about one-fourth of the way up the back side of the calf. Place ultrasound gel on the area and use the Doppler probe to find the spot where the PT pulse is the strongest.

Record the blood pressure of the PT artery. Repeat the same process that you did to find the DP artery. Once finished, record the pressure and then switch the cuff to the right leg. Record the blood pressure of the dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial arteries on the right leg.
Calculating the Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
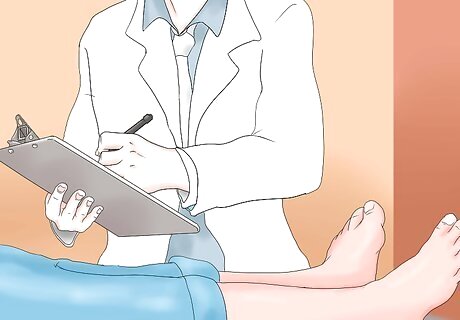
Take note of the higher systolic blood pressure of the ankle. Compare the left and right ankle readings, as well as the DP and PT artery readings of both ankles. Whichever number is the highest from each ankle will be used to calculate the ABI.

Divide the systolic blood pressure of the ankle by the systolic blood pressure of the arm. You will calculate the ABI for each leg individually. Use the highest value from your readings of the left ankle arteries and divide it by the value of the brachial artery. Then repeat this process with the results from the right ankle. Example: The systolic blood pressure of the left ankle is 120 and the systolic blood pressure of the arm is 100. 120/100=1.20.
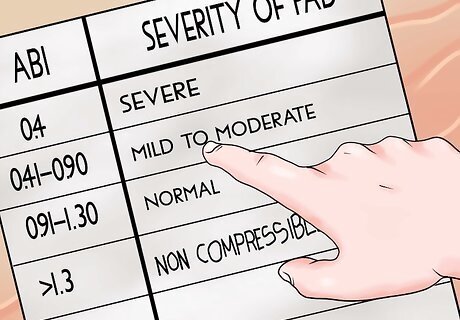
Record and interpret the result. The normal resting ankle brachial index is 1.0 to 1.4. The closer the ABI of the patient to 1, the better the result is. This means that the arm blood pressure should be as close as possible to the ankle blood pressure. An ABI of less than 0.4 suggests severe peripheral arterial disease. The patient may develop non-healing ulcer or gangrene. An ABI of 0.41-0.90 indicates mild to moderate peripheral artery disease and warrants further tests like CT, MRI, or angiography. An ABI of 0.91-1.30 indicates normal vessels. However, a value between 0.9-0.99 may cause pain during exercise. An ABI >1.3 indicates non-compressible and severely calcified vessels that artificially raise the blood pressure. Long standing diabetes or chronic kidney disease may lead to this state.

















Comments
0 comment