
views
The fundamentals of the 21st century aren’t any different from previous ones. Having a well paid job, a decent medical cover and a house that you own is what would probably be described as a Successful life even today.
As the human race goes to another level of advancement, things have become a little complicated and understanding tax benefits of home loan is crucial to reduce your tax burden. There are certain benefits of home loan that can help you reduce your taxable income in a number of ways.
Section 80C: The Principal Amount Story
The Government of India has structured the bricks in a systematic manner and the repayment of the actual borrowed amount or the principal comes under the umbrella of Section 80C of IT (Income Tax) Act. The current deduction is raised to ₹1,50,000 from the previous amount of ₹1,00,000 since Budget 2014.
The Section 80C also approves the payment for registration fee and stamp duty to be claimed as a deduction from taxable income.
However, tax benefits of Home Loan under Section 80C are considered as a legitimate exercise only once the construction is complete and the certificate for the same has been awarded to you.
There's another clause that talks about transfer of the residential property on which the individual has claimed tax deduction under Section 80C. If you transfer the property before the end of 5 years from the FY (Financial Year) you had taken its possession no tax benefits on the same shall be awarded and the amount claimed as deduction in the previous years will become taxable in the year when the property is transferred.
Section 24: The Interest Story
The maximum deduction limit to be claimed from the Interest paid on home loan has been raised to ₹2,00,000 from the previous ₹1,50,000 allowed under Section 24 of a self-occupied property. There’s also a possibility that the property is not self occupied and the individual is staying at another place due to his employment or business, then, a fixed amount of ₹2,00,000 shall be considered for deduction.
In case the property is not self occupied but rented, the rent received will be considered as Income and the Interest paid will be claimed under deduction. If the individual’s interest paid is more than rent then it can be set off as Loss from House Property and can be deduction from the taxable income.
The deduction must be claimed on a yearly basis when the interest had accrued and that's the main difference between the Section 24 and 80C (where deduction is claimed when principal amount is paid)
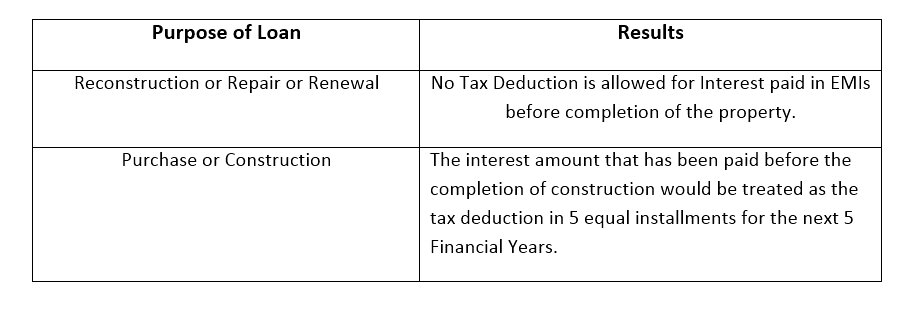
Treatment of Pre-Construction Interest
The new trend is all about EMIs and the mayhem begins even before the construction is complete. So if you’ve taken a home loan for a property that is under construction then the following rules apply:
Section 80EE: The First Time Home Buyers
In Budget 2016, Section 80EE was reintroduced to give additional ₹50,000 benefit to first time home buyers over and above the ₹1,50,000 limit under Section 80C and ₹2,00,000 limit under Section 24.
Deduction under Section 80EE can be claimed only if the value of property is less than ₹50 Lakh and home loan taken on it is less than ₹35 Lakh.
Secondly, the home loan must have been sanctioned after 1st April 2016.
How to Claim Tax Benefits from Home Loan?
You need to furnish the Interest Certificate from the Bank and a Loan Account Statement that clearly mentions the amount paid towards Principal, Interests and Prepayment of Principal (if any).
To Sum Up
The above mentioned points are a brief about the tax benefits of home loan. A lot of people are saving their taxes by spending and investing wisely. Join the league and be a super tax saver.




















Comments
0 comment