
views
Check if your computer is under warranty. Before attempting to make any repairs yourself, check to see if your computer is under warranty. In many cases, simply opening your computer will void your warranty. If your computer is still under warranty, then it is recommended that you contact the point of sale or manufacturer and have them repair your computer for you. If you built the computer yourself you'll want to see if your motherboard is still under warranty.
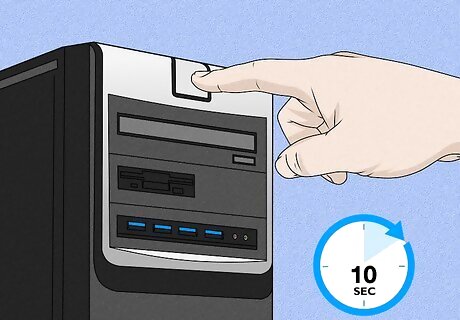
Boot from the backup BIOS (Gigabyte motherboards only). Some Gigabyte motherboards come with a backup BIOS installed on the motherboard. If the main BIOS is corrupted, you can boot from the backup BIOS, which will automatically reprogram the main BIOS if there is anything wrong with it. If it does not boot into the backup BIOS automatically, you can use one of the following steps to force it to boot from the backup BIOS: Method 1: Power your computer off. Then press and hold the power button until your computer powers back on. Continue to hold the power button until the computer powers off again. When you power it back on, it should boot from the backup BIOS. Method 2: Power your computer off. Press and hold the Power button and the Reset button for about 10 seconds and release. When you power your computer on a third time, it should boot from the backup BIOS. Method 3: Use this method as a last resort. If you are unable to get your Gigabyte motherboard to boot into the backup BIOS using either of the two methods above, you'll need to open your computer and access the motherboard directly. Look for a chip labeled "m-BIOS" or "Main BIOS" or something similar. Use a wire or a paperclip to short Pins 1 and 6 on the chip. There should be a triangle icon or a red dot next to Pin 1 (it's usually the one on the bottom right). Pins 1, 2, 3, and 4 are all on the same side. Pin 5 is directly across from Pin 4 and Pin 6 is right next to Pin 5. Place a paperclip or short piece of wire on Pins 1 and 6 and hold it steady (be sure to touch something metal before touching the inside of a motherboard.) Have another person power the computer on. Remove the paperclip or wire when you hear it beep. This should force your computer to boot into the backup BIOS.
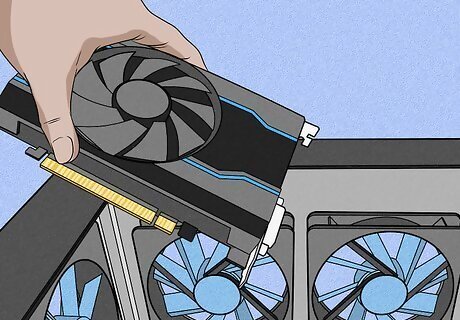
Remove the dedicated graphics card. Some users have reported that problems with the BIOS can be fixed by removing the dedicated (discrete) graphics card and forcing your PC to utilize the integrated graphics card. Note: Not all CPUs come with an integrated graphics cards. These include Intel CPUs with an F product line suffix. For more information, check your manufacturer's product webpage. Warning: Conducting repairs on your PC requires that your PC is powered off all the time. Be sure to keep your hand on something metal outside your computer or wear static wristbands to keep yourself electrically earthed. This prevents static discharge that can cause permanent damage to your computer.
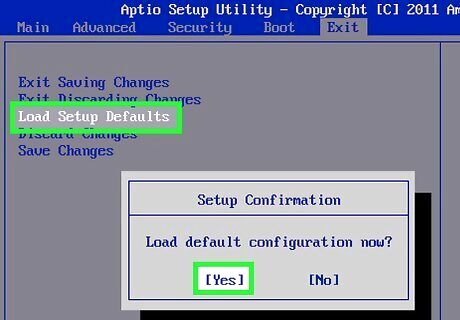
Reset the BIOS. In some cases, you may be able to fix problems with a corrupted BIOS by resetting the BIOS. You can do this one of three ways: Boot into the BIOS and reset it to the factory settings. If you are able to boot into the BIOS, go ahead and do so. Locate the option to "Load Setup Defaults", "Restore Factory Settings", or something similar. Select this option to reset the BIOS. Remove the CMOS battery from the motherboard. Unplug your computer and open your computer's case to access the motherboard. It's the large board that has all the cables, chips, and computer cards attached to it. Locate the CMOS battery. Generally, it is a type CR2032 battery that is about the size of a quarter. Carefully remove the battery and let it sit for 20 minutes. If your computer is a laptop, remove the laptop battery as well. If this doesn't fix the issue, try replacing the battery with a new one. Reset the jumper. This is typically done on older motherboards. Unplug your computer and open your computer's case to access the motherboard. Locate a jumper cable that says "CMOS" or something similar next to it. The jumper will be placed on two out of three pins. Remove the jumper and replace it one set of pins over. Press and hold the Power button on the computer for about 15 seconds. Replace the jumper back to it original position.

Update your BIOS. In some cases, you may be able to fix problems with a corrupt BIOS by updating the BIOS. Make sure your computer has a consistent power source when you updating your BIOS. If the update process is interrupted, it can cause permanent damage to your computer. You will need to know which version of BIOS you are running. Use the following steps to update your BIOS: Find out which version of BIOS you are running. If you are able to boot into your BIOS, it will tell you what version of BIOS it is running. If you can boot into Windows, click the Windows Start menu and type "System Information" and open the System Information app. Check what version of BIOS you are running next to "BIOS Version/Date." If you cannot boot into the BIOS or Windows, you most likely will not be able to update your BIOS. Consult your computer manufacturer's website. You can do this from a separate computer if need be. Download an updated BIOS file and copy it to a flash drive. Follow the manufacturer's instructions to update your BIOS. The process will be a little different from one computer manufacturer to another. In most cases, you will need to copy the BIOS update file to a flash drive or create a bootable flash drive. You will either boot from the bootable flash drive or boot into the BIOS and select the option to update the BIOS from a flash drive. If you have an HP computer, you may be able to update the BIOS shutting down your computer and then pressing Windows key + B + Power and hold them for about 3 seconds. Release the Power button, but continue to hold the Windows key and B buttons until the BIOS update screen appears. Your computer screen may go blank and you may hear more beeping sounds coming from your computer.
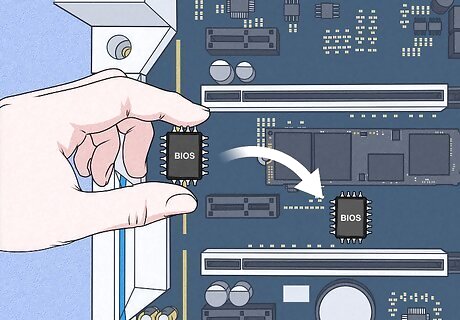
Replace the BIOS chip. This is only an option if your motherboard has a slotted DIP or PLCC BIOS chip. If the BIOS chip is soldered to the motherboard, your only option will be to replace the motherboard. If you are able to replace the BIOS chip, use the following steps to replace it: Take note of the make and model of your motherboard. Purchase a replacement BIOS chip for the motherboard model that you have. You can purchase BIOS chips online from eBay, or a specialty website like, Newegg, or BIOS-Chip24. Some places may require that you send them your old BIOS chip to be reprogrammed. Locate the BIOS chip on the motherboard and note which end the notch is facing. Carefully remove the old BIOS chip using an extraction tool or by carefully prying it loose using a small pick or jewelers flathead screwdriver. Insert the new BIOS chip so the notch faces the same direction as the notch on the old BIOS chip. If the prongs are too wide, you can carefully bend them inward by press pushing them against a solid flat surface.
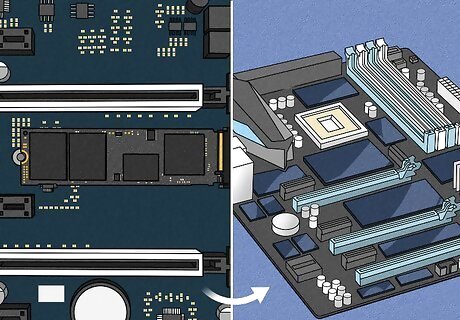
Replace the motherboard. If you cannot replace the BIOS chip, and you can't reprogram it or fix the problem by resetting it, then the only option is to replace the motherboard. You can purchase a new motherboard from Amazon, eBay, or any computer specialty store such as Newegg.com.


















Comments
0 comment