views
Determining Where the Bleeding Might Be Coming From
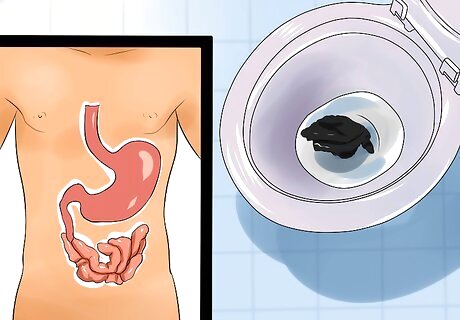
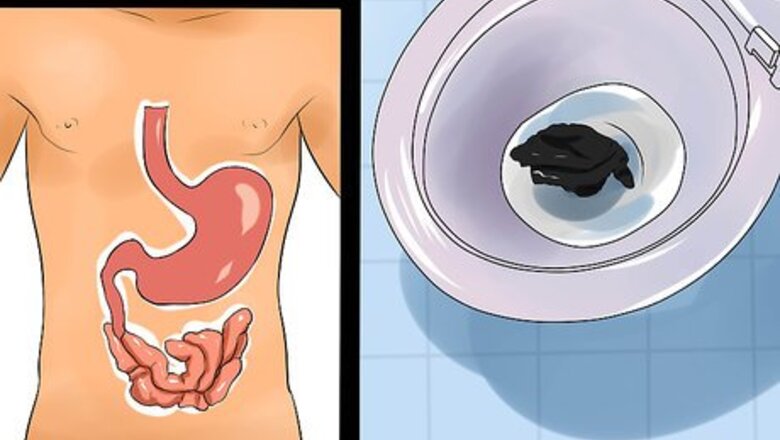
Identify black stools or stool that looks like it contains tar. It may seem gross to examine the color of your stool, but it will provide important information. And your doctor will probably want to know what you saw. Dark stool is called melena. It indicates that the blood is coming from your esophagus, stomach, or the beginning of the small intestine. Causes include problems with the blood vessels, a tear in your esophagus, a stomach ulcer, inflammation of the stomach lining, blood supply being cut off to part of the intestines, an injury or object that is stuck in your digestive tract, or abnormal veins in your esophagus or stomach, called varices.
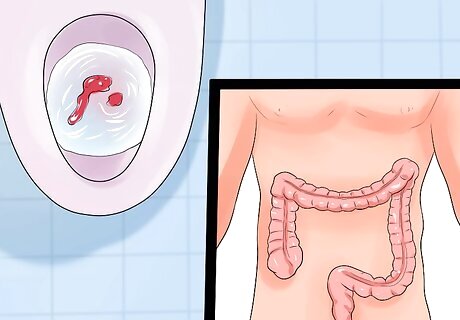
Notice if your stool is red. This is called hematochezia. It means that you are bleeding from lower in your digestive tract. Possible causes include: problems with the blood vessels or blood supply getting cut off in the small intestine, large intestine, rectum, or anus; a tear in the anus; polyps in the colon or small intestine; cancer in the colon or small intestine; infected pouches in the colon called diverticulitis; hemorrhoids; inflammatory bowel disease; an infection; an injury; or an object that is stuck in your lower digestive tract.
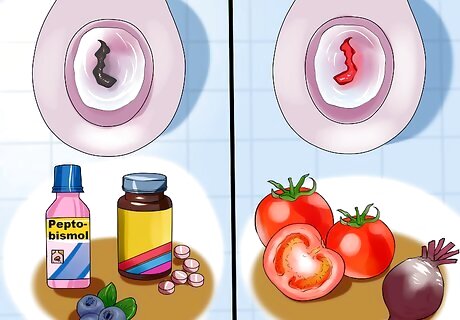
Consider whether it could be something other than blood in your stool. It could be something you ate. If your stool is black, possible causes include black licorice, iron pills, Pepto-Bismol, beets, and blueberries. If your stool is red, it could be from beets or tomatoes. If you aren’t sure, the safest thing to do is to bring a sample to the doctor and they can test it to determine if you are actually passing blood.

Evaluate whether you are on medications that may cause bleeding in the digestive tract. Even over-the-counter drugs can cause bleeding if taken in large amounts or for a long time. If this could be your situation, you should go to the doctor to discuss changing your medications. Medications that can do this include: Blood thinners like aspirin, warfarin, and clopidogrel Some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs which include ibuprofen or naproxen
Seeking Medical Attention

Give your doctor as much information as possible. Your doctor will want to know: How much blood? When did it start? Could it be an injury? Have you choked on anything recently? Have you lost weight? Do you have any symptoms of infection such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, or diarrhea?
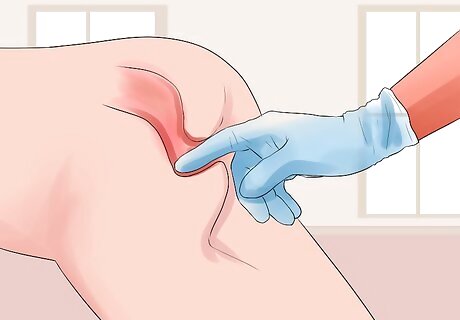
Expect your doctor to examine your rectum. This may seem strange, but it will probably be necessary. During a rectal exam, the doctor will feel inside your rectum with a gloved finger. It will be quick and painless.
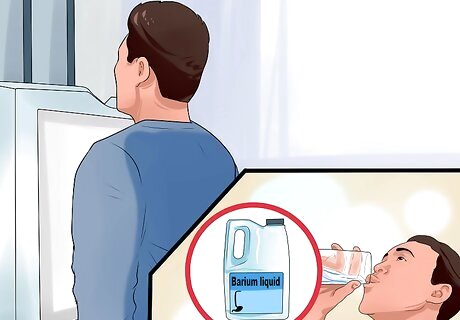
Get additional tests to pinpoint the problem. Depending on what the doctor suspects the cause is, he or she may recommend some of the following tests: Blood work. An angiography. The doctor injects you with dye and then uses x-rays to see the arteries. Barium studies in which you swallow barium, which then shows up on an X-ray and lets the doctor see your digestive tract. A colonoscopy. An EGD or esophagogastroduodenoscopy. The doctor will put a scope down your throat to look at your esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. A capsule endoscopy in which you swallow a pill containing a video camera. A balloon-assisted enteroscopy in which the doctor can look at difficult-to-see areas of the small intestine. An endoscopic ultrasound that has an ultrasound device attached to the endoscope. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to form a picture. An ERCP or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography which uses an endoscope and x-ray to see the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas. Multiphase CT enterography to view the walls of the bowels.
Stopping the Bleeding

Allow minor problems to heal naturally. Problems that often heal without intervention include: Hemorrhoids, also called piles, which may be swollen or itchy. An anal fissure, which is a small tear in the skin around the anus. It is painful and may take a few weeks to heal. A viral or bacterial infection, called gastroenteritis, will often heal on its own if you stay hydrated and allow your body to fight it. Low fiber diets can cause straining when you are passing stools. A diet rich in fiber will reduce straining when you go to the bathroom, making stool passage easier.

Treat infections with antibiotics. This is often necessary for diverticulitis. Antibiotics will help clear bacteria out of the pouches and bulges in your bowels. Your doctor may recommend eating only fluids for a few days to reduce the amount of feces your digestive tract must process.
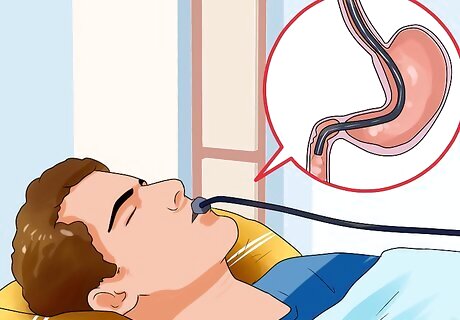
Treat ulcers, abnormal blood vessels, and other tissue problems with a variety of different interventions. There are several methods which involve using an endoscopy to treat the damaged tissue: An endoscopic thermal probe uses heat to stop the bleeding, particularly for an ulcer. Endoscopic cryotherapy freezes abnormal blood vessels. Endoscopic clips will close an open wound. Endoscopic intracranial cyanoacrylate injection uses a type of glue to seal a bleeding blood vessel.
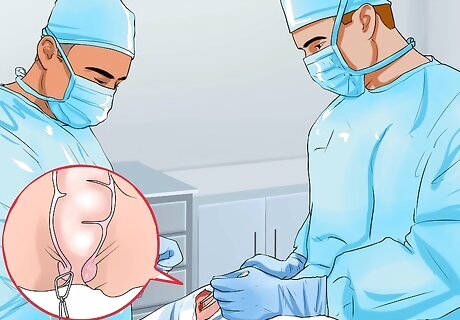
Consider surgery if the bleeding is serious or returns. Conditions that are often treated with surgery include: An anal fistula, where a passage forms between the bowels and the skin near the anus. This often happens after an abscess bursts. It usually doesn't heal without surgery. Recurrent diverticulitis. Bowel polyps. These are small bumps that are usually not cancerous, but usually need to be removed.
Consult your doctor about Histamine 2 blockers and omeprazole. If your bleeding is caused by an ulcer or by gastritis, these medications may be able to treat your underlying condition. Talk to your doctor to see if a prescription is right for you.

Take iron supplements to treat anemia. Rectal bleeding, if severe, may cause anemia because of the blood loss. If you are feeling dizzy, fatigued, lightheaded, or weak, you should visit your doctor to get tested for anemia. Most mild forms of anemia can be treated by taking iron supplements
Fight bowel cancer aggressively. The treatments vary based upon where it is located and at what stage it is. Possible options include: Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Medications



















Comments
0 comment