
views
X
Research source
Use these tips to learn how to calculate normality.
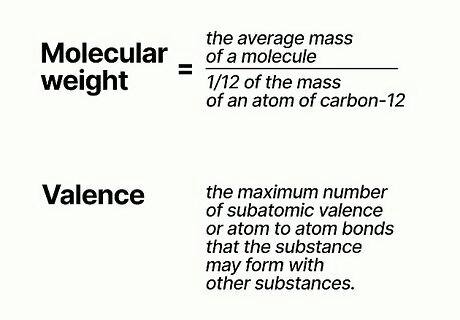
Gather information about the equivalent weight of the reacting substance. Consult chemical reference books to find out the valence and the molecular weight of the substance. Molecular weight is the ratio of the mass of 1 molecule of the substance to the mass (one carbon12 molecule divided by 12.) Valence is determined by the maximum number of subatomic valence or atom to atom bonds that the substance may form with other substances. This information will be required to determine normality.
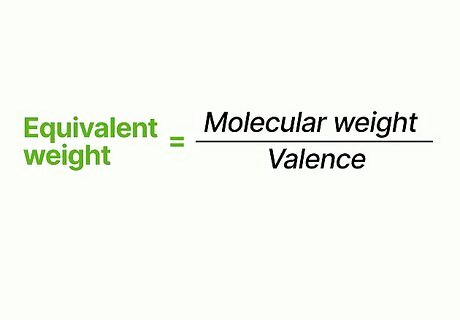
Figure the equivalent weight of the substance. The equivalent weight of the substance is equal to the molecular weight divided by the valence.

Calculate normality. Normality is the concentration of the substance of interest in a dissolving liquid. Therefore, normality is a property of the mixture, and will vary with the use of more or less dissolving liquid to place the substance of interest into a solution. Normality is the number of grams of the substance of interest divided by (the equivalent weight of the substance times the amount of dissolving liquid).

Try an example. Dissolve sodium chloride (NaCl) in water. Sodium chloride has a valence of 1 and a molecular weight of 58.443. Therefore, the equivalent weight is 58.443/1 or 58.443. 1 gram of NaCl is dissolved into 0.05 L of water, so the normality of the solution is 1/(58.443 x 0.05) or 0.342.

















Comments
0 comment