views
- Use "rpm -i packagename.rpm" to install a package.
- To delete a package, use "rpm -e packagename.rpm."
- You can use other flags with the rpm command to test installations, specify install paths, and more.
Installation
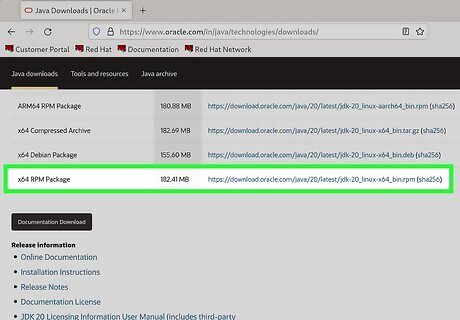
Download your desired RPM package. There are many RPM depositories on the Internet, but if you're looking for Red Hat RPM packages, you can find them here: The Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation media, which contain many installable RPMs. The initial RPM repositories provided with the YUM package manager. The Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) provides high-quality add-on packages for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
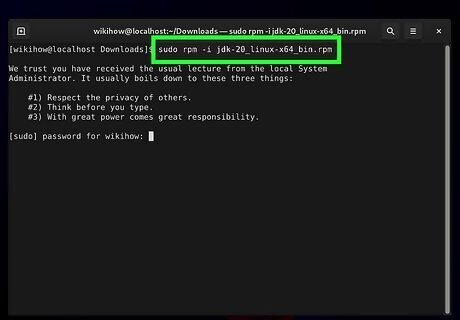
Install the RPM package. Once downloaded, you have two options: Double-click the package. A package management window will appear with instructions to guide you through the process. Open a terminal window, and type rpm -i *package_location_and_name* (without the spaces in and )
Helpful RPM Flags
The rpm -i command syntax is listed below.
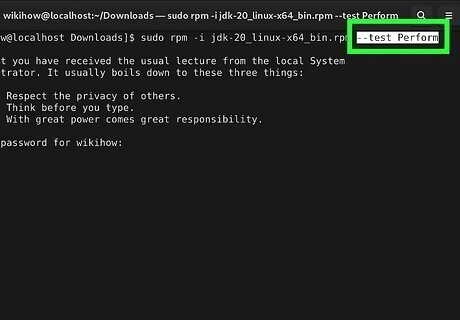
Install-specific options:
-h (or --hash) Print hash marks ("#") during install
--test Perform installation tests only
--percent Print percentages during install
--excludedocs Do not install documentation
--includedocs Install documentation
--replacepkgs Replace a package with a new copy of itself
--replacefiles Replace files owned by another package
--force Ignore package and file conflicts
--noscripts Do not execute pre- and post-install scripts
--prefix
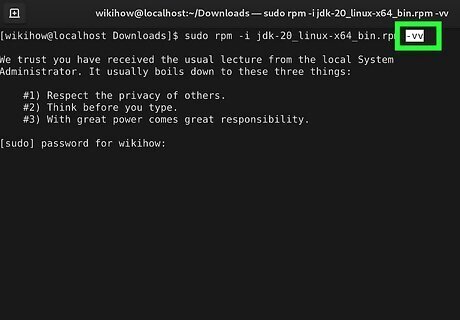
General Options.
-v Display additional information
-vv Display debugging information
--root


















Comments
0 comment