
views
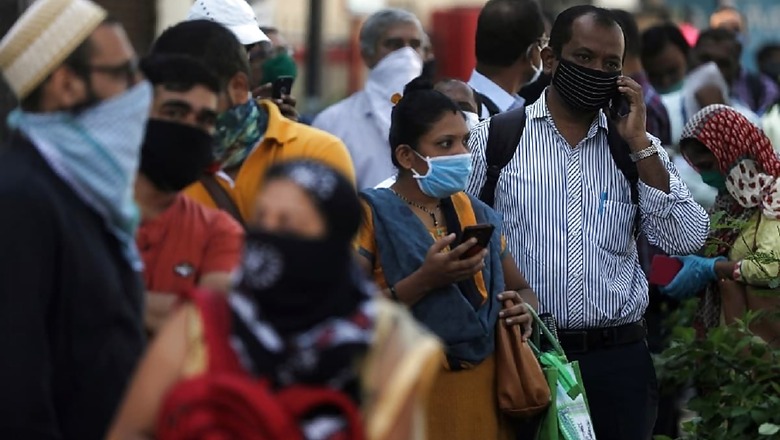
A sero study revealed that nearly half of Karnataka’s population was infected with the deadly coronavirus by the end of August. The study also indicated that at least 44.1 per cent of the population in rural areas and 53.8 per cent in urban areas were exposed to Covid-19, therefore developed antibodies for the infection.
The study- ‘Prevalence of COVID-19 In Rural Versus Urban Areas in a Low-Income Country: Findings from a State-Wide Study in Karnataka, India’ is based on data collected from a representative sample of households in 20 districts from mid June to August.
The IDFC institute, Mumbai, carried out the comprehensive Covid-19 seroprevalence study. Researchers from the institute undertook the statewide study in collaboration with the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy. Funded by the ACT Grants (India), it was led by Professor Manoj Mohanan from Duke University, Professor Anup Malani from Chicago University, and Anu Acharya from Mapmygenome along with Kaushik Krishnan from the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy.
The study found out that the state alone has 31.5 million Covid-19 cases with 44 per cent of rural and 54 per cent of the urban population affected. And it was conducted in a random population for measuring the spread of the Covid-19 pandemic. The presence of antibodies typically suggests that people infected with a virus would gain immunity for some period of time.
Researchers stated that among the two reasons for widespread infection were, the rural areas experienced fewer restrictions on mobility and the release of the lockdown imposed in March was immediately followed by an influx of large migration of daily labourers, Indian Express reported. These migrant labourers lost their sources of income in urban centres returning to hinterland after lost job opportunities.
The Karnataka Seroprevalence Study (KSS) drew a random sample from CPHS’s 9,717 households in the state separately for the urban and rural strata. Karnataka roughly has a population of 64 million.
Reportedly, based on the government mid-year 2020 population estimates, adjusted seroprevalence across Karnataka implies that approximately 31.5 million residents have been infected, 96.4 times the 3,27,076 publicly reported cases as of August 29. Meanwhile, the estimated RT-PCR positive tests suggested that the infections surged rapidly during August. The proportion of those testing positive on RT-PCR ranged from 1.5 to 7.7 per cent in rural areas and 4.0 to 10.5 per cent in urban areas, suggesting a rapidly growing pandemic.
Researchers also stated that a total relaxation could lead to a whopping spike in infections among such at-risk populations leading to further spikes in severe cases or mortality which would create a large burden for the healthcare system.
Read all the Latest News, Breaking News and Coronavirus News here
















Comments
0 comment