views
The way you navigate and do all the complex location stuff using apps on your smartphones is set to undergo its biggest change in years. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has developed NavIC Technology that will perhaps be integrated in the next Android phone that you buy. Qualcomm has introduced the new Snapdragon 720G, Snapdragon 662 and Snapdragon 460 processors, designed for budget and mid-range Android smartphones, and will use NavIC positioning system for location services. This is the first time the NavIC technology has been introduced in new chips by Qualcomm. NavIC is the Indian version of the global positioning system (GPS) that we have used over the years, and ISRO has collaborated with chip maker Qualcomm to integrate this in the line of chipsets that they make.
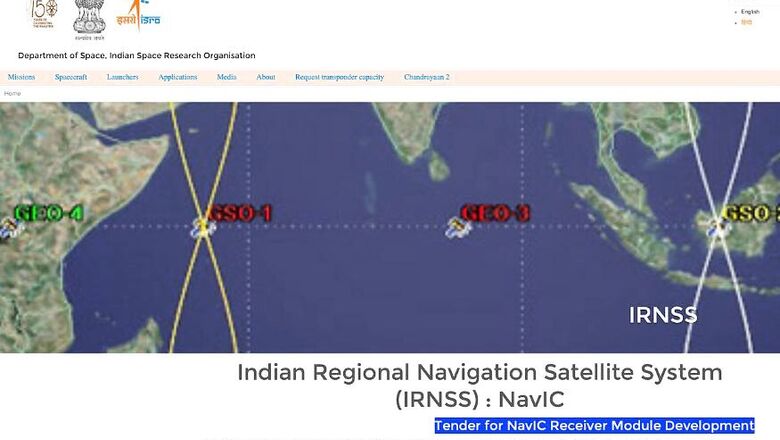
NavIC is the operative name for what is otherwise known as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS). It has been developed and designed for NavIC was developed for terrestrial, aerial and marine navigation, as well as provide location tracking during disaster management and for vehicle tracking as well as commercial fleet management scenarios. It has primarily been designed to work on smartphones. NavIC will provide two types of location services—the standard positioning service as well as the encrypted service for security agencies as well as military access. “Qualcomm has announced that its chip is going to have NavIC and they are releasing it. Now almost Xiaomi is in agreement to have it. Xiaomi may launch its mobile phones with NavIC chipsets,” the ISRO official told PTI. At this time, 3GPP, the 3rd Generation Partnership Project standards organization which develops protocols for mobile telephony, has already approved the system.
The NavIC system will rely on 7 satellites, of which 3 are geostationary earth orbit (GEO) satellites and 4 are geosynchronous orbit (GSO) satellites. Each satellite has 3 rubidium atomic clocks, which will provide accurate location data. This system will be available to any smartphone which a compatible NavIC receiver hardware within a range of 1,500 kms around India, called the Primary Service Area. The IRNSS 1-G satellite, the 7th in this constellation, was launched in September 2017. It is estimated that NavIC will have an accuracy better than 20 meters.
The GPS satellite-based radio navigation system is owned by the United States and operated by the United States Air Force, has 24 satellites in orbit. India now joins the group of countries that have their own positioning system, which includes Russia (GLONASS), the European Union (Galileo) and China (BeiDou Navigation Satellite System).


















Comments
0 comment