Tech Talk | National Strategy for Robotics to Shake Up Sectors, Balance Human Workforce & Automation

views
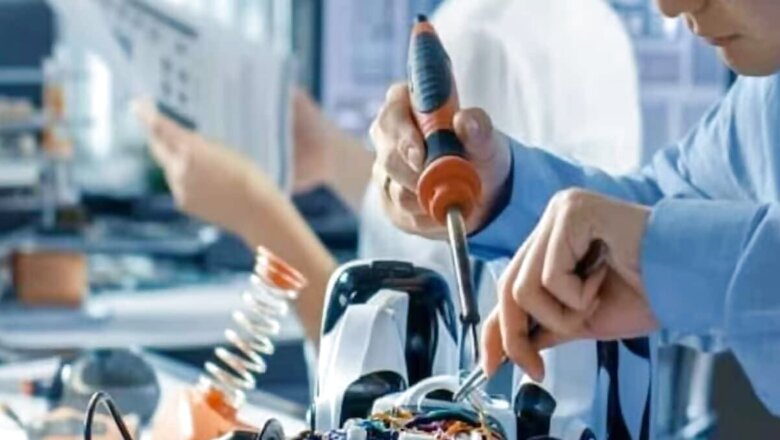
The Ministry of Electronics and IT has invited public comments on the Draft National Strategy on Robotics, which is poised to revolutionise several sectors, leveraging cutting-edge technology to drive economic growth and improve the quality of life.
The strategy, also known as the National Robotics Mission, encompasses a whole ecosystem approach, involving industry, academia, and start-ups. One of its overarching goals is to position India as a global leader in the development and adoption of robotics. This ambitious mission aligns with India’s broader vision for Artificial Intelligence-enabled technologies across sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and national security.
Impact on Agriculture and Labour Force
In the agriculture sector, which employs a significant portion of India’s workforce, robotics holds the promise of boosting productivity and addressing safety concerns. The National Strategy for Robotics acknowledges the need to find a ‘fine balance’ between human labour and automation. It recognises that while automation can improve efficiency, it should also safeguard the well-being of farmers. Occupational hazards in traditional farming such as musculoskeletal disorders and exposure to harmful chemicals underscore the urgency for modernisation and improved safety measures.
“Building on this momentum, robotic automation in the agriculture sector aimed at maximising productivity and addressing safety risks to farmers’ welfare may be undertaken,” suggests the draft. Potential use cases include crop scouting and spot-spraying robots. These robots can help detect pest attacks and diseases early, preventing crop damage, while minimising the need for manual labour.
National Security and Technological Excellence
India’s defence sector, one of the world’s largest, faces challenges in border management and real-time intelligence collection. The strategy recognises the importance of technological excellence in maintaining national security. In this case, the draft suggests leveraging robotic automation to address these challenges.
The “Sapper Scout” UGV (Unmanned Ground Vehicle) for mine detection is highlighted as an example of the potential of robotics in defence. It can detect and mark mines, reducing the risks to human personnel. Surveillance robots are also mentioned as tools for enhancing border security.
Balancing Automation and Human Labour in Workforce
The National Strategy for Robotics stresses the need for “ethical use” of robotics technology. The draft says while automation can bring numerous benefits, it must be deployed in a manner that respects human rights and is fair and transparent. Finding the right balance between automation and the human workforce is a central theme throughout the strategy.
To ensure this balance, the strategy outlines several key areas of focus. These include creating job opportunities in emerging robotics fields to absorb displaced workers, upskilling and reskilling initiatives to address the shortage of technicians with specialised training, and establishing standards and certification to ensure the quality and reliability of robotic technologies.
Adoption of Ecosystem
To drive the adoption of robotics technology, targeted demand-side interventions are proposed. These include public procurement policies to incentivise domestic production and technology adoption plans to identify and promote priority use cases. Additionally, financial incentives, international immersion programmes, and capacity-building initiatives are recommended to nurture the robotics ecosystem in the country.
Futher, as per the draft, the Robotics Innovation Unit (RIU), a new independent agency under the IT ministry, will be responsible for implementing the National Strategy on Robotics. It will aim to create a robotics ecosystem that fosters innovation, supports technology development, and drives adoption by engaging the industry, MSMEs, start-ups, individual innovators, R&D institutes, academia, and government organisations.
Overall the strategy recognises the potential benefits of robotics technology while stressing the importance of ethical use, safety, and the well-being of Indians. As India advances its robotics ecosystem, it aims to position itself as a global leader in intelligent cyber-physical systems, ushering in a new era of technological innovation and economic growth.


















Comments
0 comment